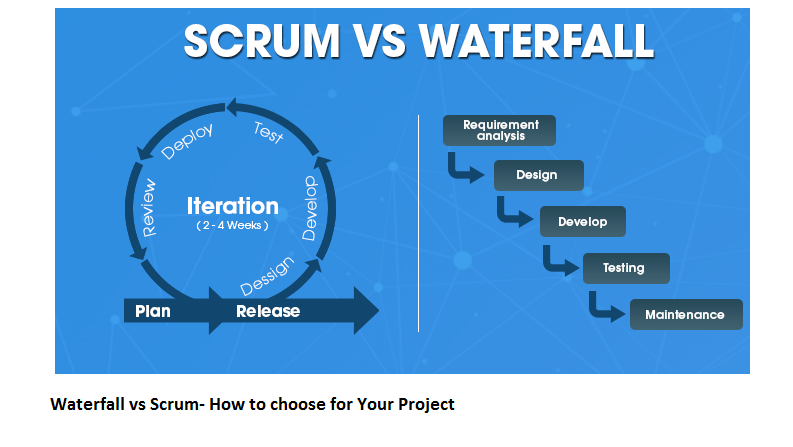
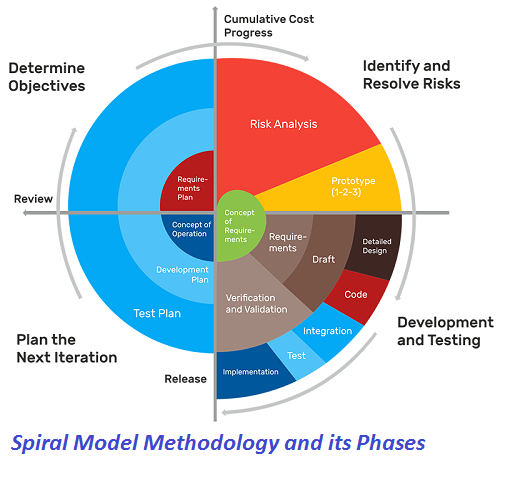
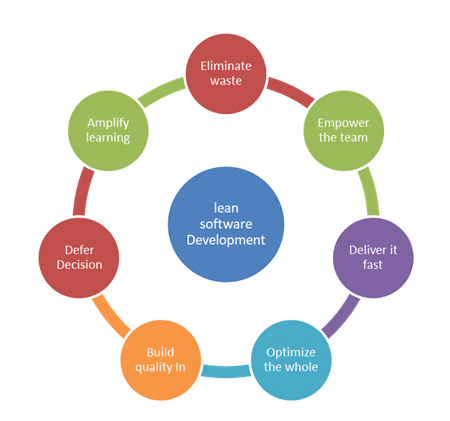
Blockchain Up Till Now
Blockchain is a distributed database present on multiple computers at the same time. It is constantly growing as new sets of recordings are added to it. A blockchain ledger consists of two kinds of records, individual transactions, and blocks. The first block consists of a header and data that pertains to transactions taking place within a set time period. The block’s timestamp is used to help create an alphanumeric string known as a hash.
blockchain-development
After the first block is created, each subsequent block in the ledger uses the previous block’s hash to calculate its own hash. The database is not managed by any individual body; instead, everyone in the network gets a copy of the whole database. Old blocks remain forever and new blocks are added to the ledger irreversibly, making it impossible to manipulate by transactions, faking documents and other information.
Satoshi Nakamoto is the name used by the unknown individual person or group of people who developed bitcoin, authored the bitcoin white paper, and created and deployed bitcoin’s original reference implementation. As part of the implementation, they also designed the first blockchain database. In the process, they were the first to solve the double-spending problem for digital currency using a peer-to-peer network. They were active in bitcoin development up until December 2010
The more popular blockchain using systems
BigChainDB, an open source system that distributes database and then adds blockchain characteristics like decentralized control for powerful query functionality, decentralized control, immutable data storage
Chain Core, a blockchain platform for issuing and transferring financial assets on an allowed blockchain infrastructure.
Corda, a distributed ledger platform with plug-able consensus.
Credits, a development framework for building allowed distributed ledgers.
Domus Tower Blockchain, designed for regulated environments, bench-marking and consuming over 1 million transactions per second.
Ethereum is an open source, decentralized, public, blockchain-based distribution computing platform.
HydraChain, an Ethereum extension for creating Allowed Distributed Ledgers for private and organization chains.
Hyperledger is an umbrella project of open source blockchains and related tools, started in December 2015 by the Linux Foundation, and supported by big industry players like IBM, Intel, SAP Ariba.
Multichain, an open-source blockchain platform, can establish and deploy private blockchains within an organization or between organizations.
Openchain, an open source distributed ledger system for issuing and managing digital assets.
Stellar, an open-source, distributed payments infrastructure that connects banks, payments systems.It’s made to move money quickly, reliably, and at almost no cost.
Blockchain Validation Algorithms
Choosing which validation algorithm to use is perhaps the most crucial aspect of selecting a blockchain platform. Generally, public platforms choose algorithms like Proof of Work because they require a lot of processing power to compute, and are easy for other network nodes to verify. There are four standard methods blockchain and other distributed database platforms used to validate.
Proof-of-work algorithm (PoW)
Practical byzantine fault tolerance algorithm (PBFT)
Proof-of-stake algorithm (PoS)
Delegated proof-of-stake algorithm ( DPoS )
Advantages and Disadvantages of Blockchain
For all its complexity, blockchain’s potential as a decentralized form of record-keeping is almost without limit. From greater user privacy and heightened security to lower processing fees and fewer errors, blockchain technology may very well see applications beyond those outlined above.
Pros
- Improved accuracy by removing human involvement in verification
- Cost reductions by eliminating third-party verification
- Decentralization makes it harder to tamper with
- Transactions are secure, private and efficient
- Transparent technology
Cons
- Significant technology cost associated with mining bitcoin
- Low transactions per second
- History of use in illicit activities
- Susceptibility to being hacked